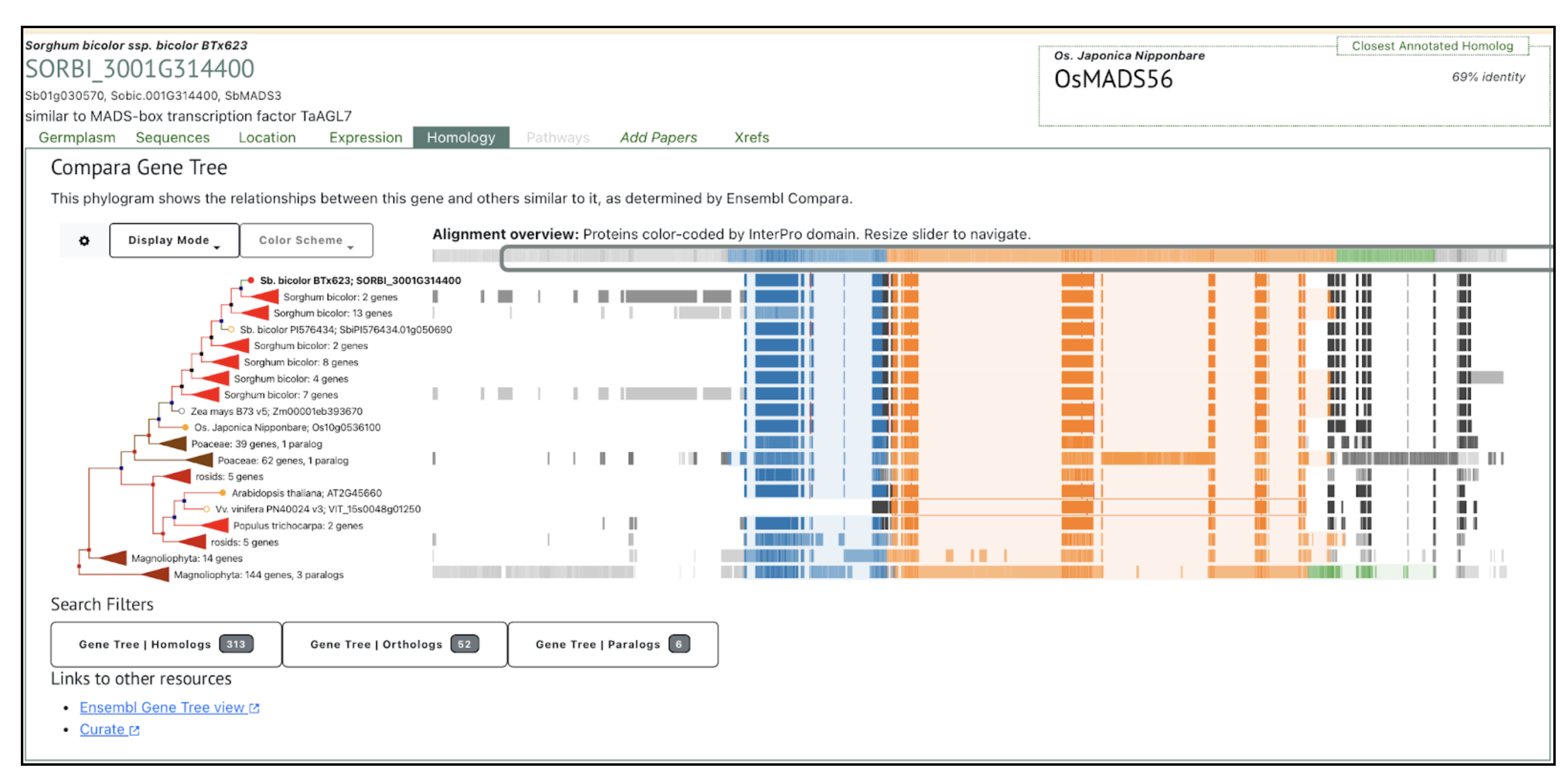
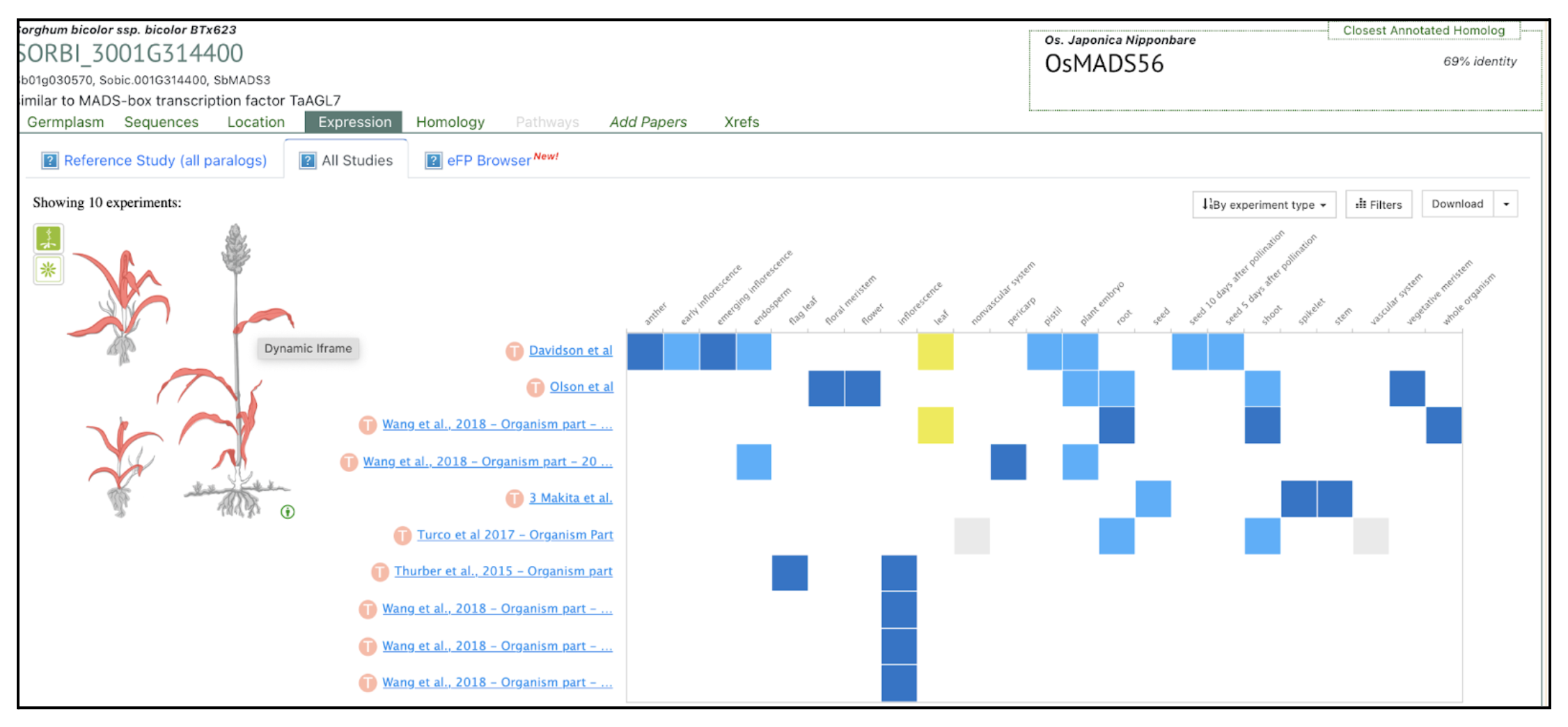
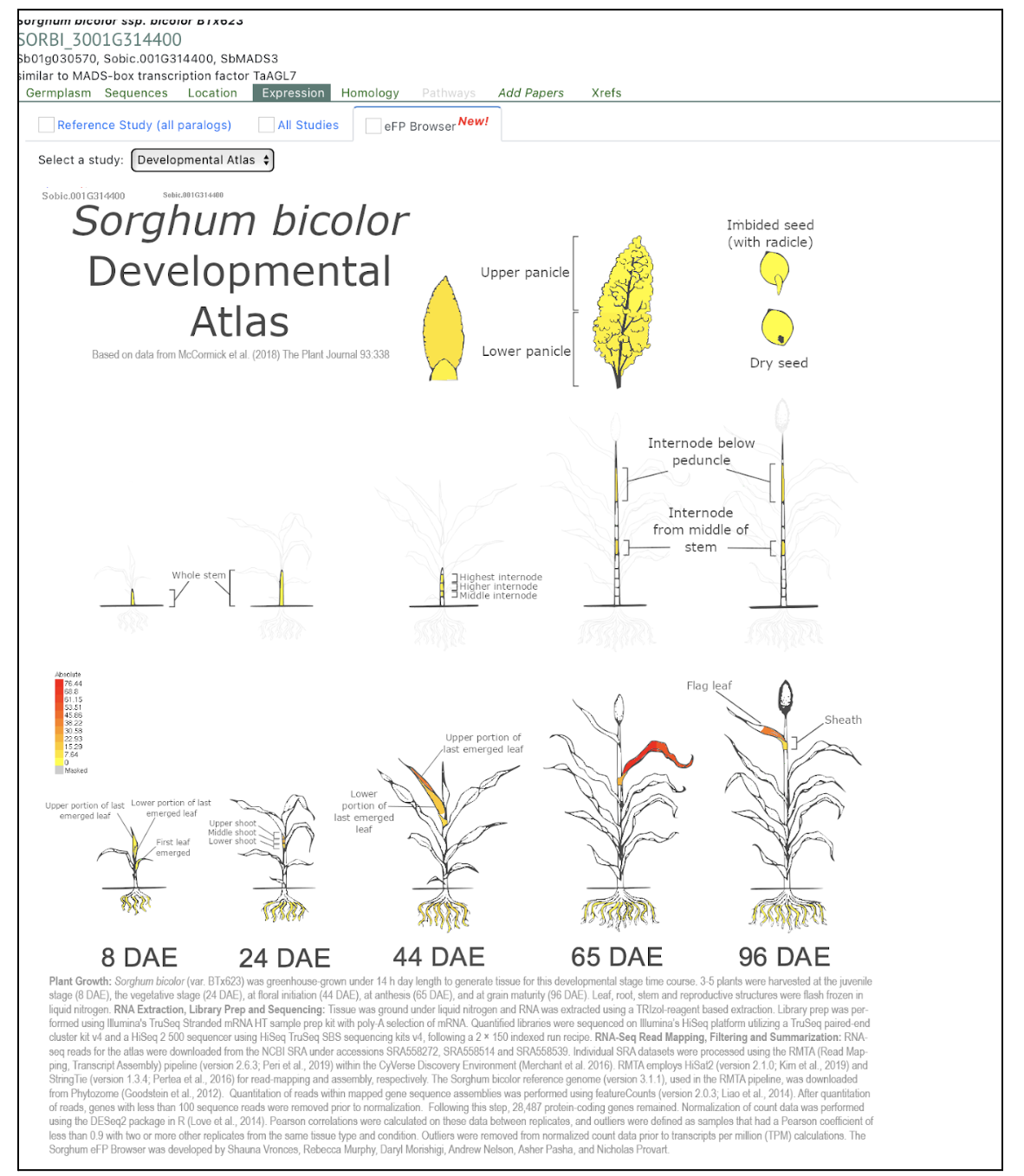
The MGS1 gene in sorghum, encoding a MIKC-type MADS-box transcription factor, regulates the multiple-grain spikelet (MGS) trait, with natural mutations like mgs19E and mgs1BA45 significantly increasing grain yield by producing adjacent double-pistil primordia.
Spikelets, the fundamental units of crop inflorescences, play a crucial role in grain number. In cereals like sorghum, spikelets typically produce a single fertile floret. However, certain sorghum germplasms exhibit the multiple-grain spikelet (MGS) trait, forming two mature grains within a single spikelet. This characteristic has potential for increasing grain yield. The MGS1 gene, encoding a monocot-specific MIKC-type MADS-box transcription factor, was identified as the key regulator of this trait by scientists from the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Sun Yat-sen University, China Agricultural University, Syngenta Group China and University of Chinese Academy of Sciences. MGS1 contains four domains responsible for DNA binding, heterodimerization, and transcriptional activation. CRISPR-Cas9 knockout lines of MGS1 (MGS1KO-1 and MGS1KO-2) revealed a significant increase in double-grain spikelets, although some floral malformations reduced seed-setting rates. Phylogenetic analysis confirmed MGS1 as an ortholog of rice OsMADS32, further supporting its role in floral organ development.
Comparative RNA-seq analysis identified 165 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) enriched in transcription factor and enzyme activity pathways, implicating MADS-box family genes like SbMADS3, SbMADS13, and SbMADS16 in floral organ determinacy. Natural mutations in MGS1, including mgs19E and mgs1BA45, were found to induce the MGS phenotype by producing adjacent double-pistil primordia, increasing grain yield by up to 43.1%. Linkage analysis confirmed MGS1 as a single recessive locus. These findings provide a genetic framework for breeding high-yield sorghum varieties using MGS1 natural variations.
SorghumBase examples:
Zhang D, Tang S, Liu F, Zhao K, Li C, Xia R, Yu F, Xie Q, Xie P. Natural variations in Multi-Grain Spikelet 1 enhance grain number in sorghum. J Integr Plant Biol. 2025 Feb 21. PMID: 39981958. doi: 10.1111/jipb.13871. Read more