Salt stress is one of the main types of abiotic stress that restricts plant growth, development and productivity. One of the largest transcription factor (TF) families in plants is the MYB family which plays many roles in biological processes including stress response regulation. Sorghum is not only an extremely important cereal crop used as food and fodder and in biofuel production, but also exhibits high tolerance to a plethora of environmental stresses including salt. However, there are genotypic differences in response to the various stresses. A previous study done by Sui et al 2015 and Yang et al 2018 identified a differentially expressed TF SbMYBHv33 which is downregulated in two genotypes of sweet sorghum M-81E (salt-tolerant) and Roma (salt-sensitive) under salt stress conditions.
In this paper, Zheng et al. investigated the expression pattern, subcellular localization and transcriptional activity analysis to probe the function of SbMYBHv33 and performed qRT-PCR on transport related genes to study the ABA pathway and the expression of salt stress related genes. They found that overexpression of SbMYBHv33 in sorghum significantly reduced
sorghum biomass accumulation at the seedling stage and also salinity tolerance. To confirm these results the researchers performed a heterologous transformation of Arabidopsis with SbMYBHv33 and, as expected, the resultant plant lines also had reduced biomass and saline tolerance. Conversely, longer roots and increased salt tolerance were found when there was a loss of function of the Arabidopsis homolog of SbMYBHv33. This provides strong evidence that, in sorghum, SbMYBHv33 plays a vital role in growth, development and salt stress tolerance.
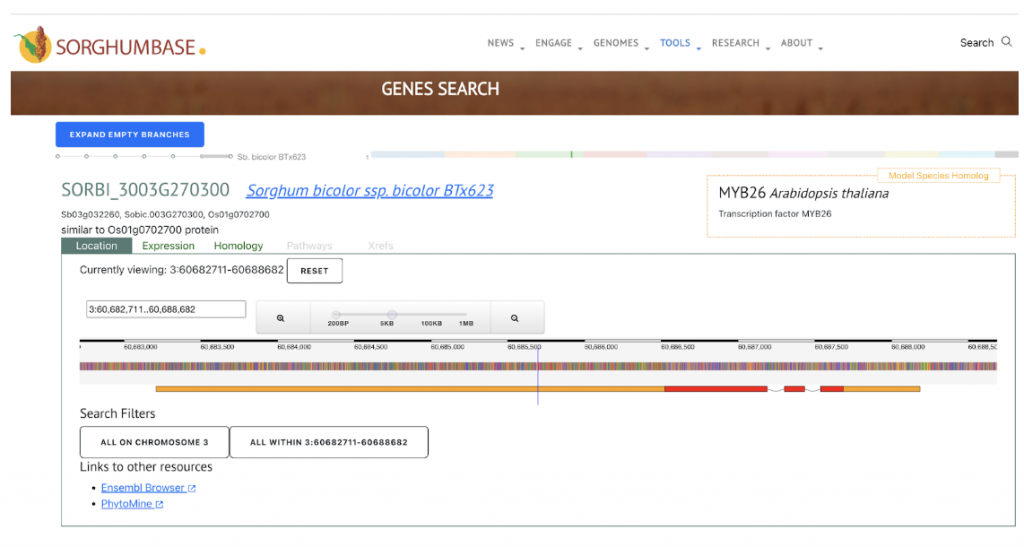
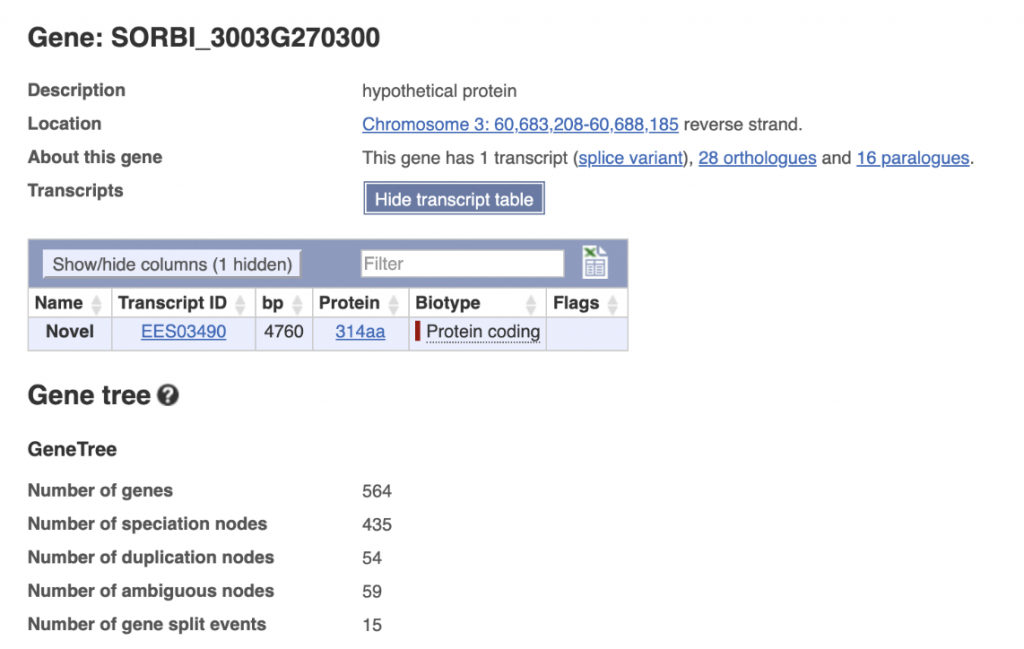
SorghumBase examples:


Reference:
Zheng H, Gao Y, Sui Y, Dang Y, Wu F, Wang X, Zhang F, Du X, Sui N. R2R3 MYB transcription factor SbMYBHv33 negatively regulates sorghum biomass accumulation and salt tolerance. Theor Appl Genet. 2023 Jan;136(1):1-14. PMID: 36656365. DOI: 10.1007/s00122-023-04292-3. Read more