In this study, the researchers investigated the impact of salt stress on plant growth and development, focusing on the role of MYB transcription factors (TFs), particularly in Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench. They identified 210 MYB genes in sorghum, distributed across ten chromosomes and divided into six subfamilies. The study focused on SbMYBAS1 (SbMYB119), which exhibited decreased expression under salt stress conditions.
Further experiments revealed that SbMYBAS1 is located in the nucleus, and overexpression in Arabidopsis plants led to reduced growth, chlorophyll content, and increased membrane permeability, malondialdehyde (MDA) level, and Na+/K+ ratio under salt stress.
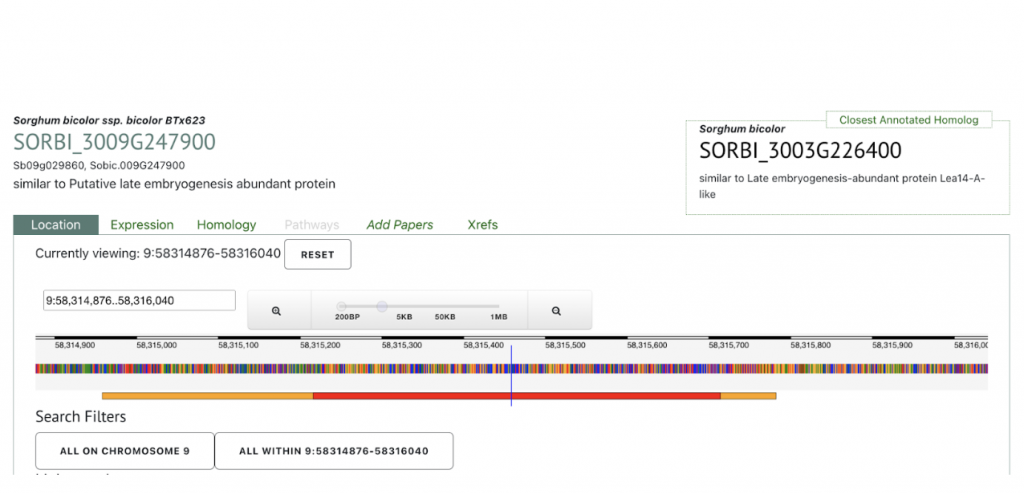
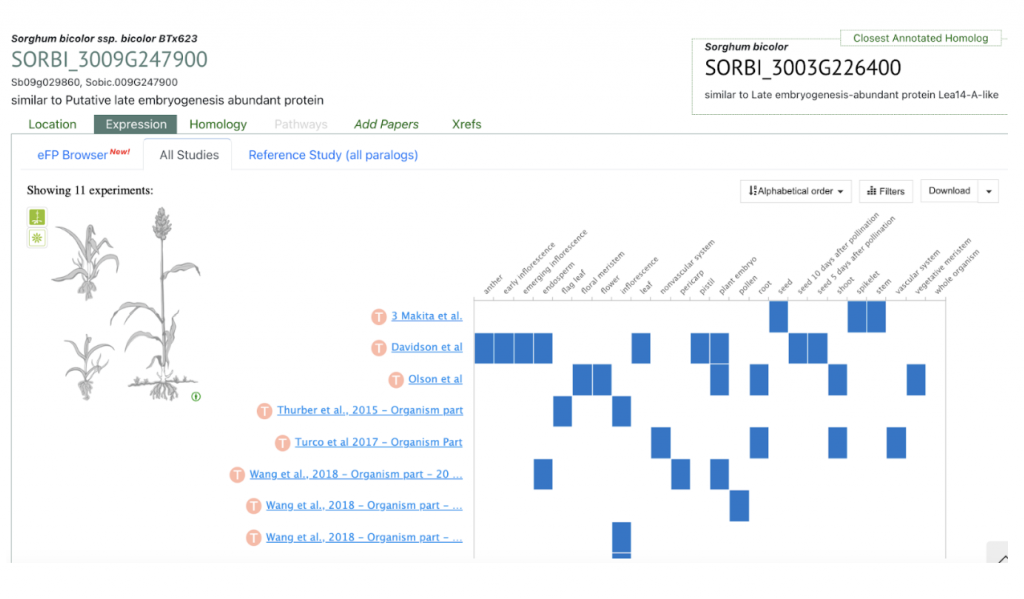
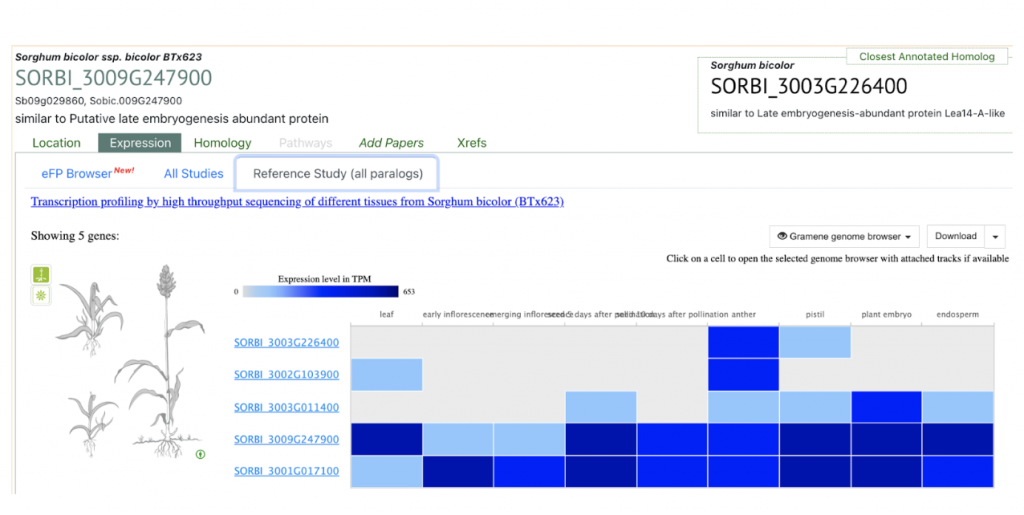
Yeast two-hybrid screening identified potential interactions between SbMYBAS1 and proteins encoded by three potential SbMYBAS1 interacting genes (SORBI_3002G184600, SORBI_3009G247900, and SORBI_3004G59600). SORBI_3002G184600 encodes trehalose-phosphate phosphatase 6, related to sugar signal transduction; SORBI_3009G247900 encodes the late embryogenesis abundant protein Lea14-A, related to oxidative stress, and osmotic stress; whereas SORBI_3004G059600 is uncharacterized, and its Arabidopsis homolog At5G21050 encodes DNAse I-like superfamily protein that might be related to the regulation of inorganic phosphate in root response to salt stress.
The study provided insights into the response mechanism of the sorghum MYB gene family to salt stress, emphasizing the importance of MYB TFs in regulating plant responses to environmental challenges. The findings contribute to the understanding of salt tolerance in plants and suggest potential avenues for improving salt tolerance in sorghum plants, with potential implications for enhancing crop yields under stressful conditions.
SorghumBase examples:
SyMBYAS1 interacting gene SORBI_3009G247900 that encodes the late embryogenesis abundant protein Lea14-A was used to explore SorghumBase below.


Reference:
Lu M, Chen Z, Dang Y, Li J, Wang J, Zheng H, Li S, Wang X, Du X, Sui N. Identification of the MYB gene family in Sorghum bicolor and functional analysis of SbMYBAS1 in response to salt stress. Plant Mol Biol. 2023 Nov;113(4-5):249-264. PMID: 37964053. doi:10.1007/s11103-023-01386-w. Read more.