Zhang et. al. used QTL mapping to identify key genetic traits in sorghum that improve grain characteristics for Maotai-flavor liquor production, offering insights for targeted breeding.
Keywords: Candidate genes, Genetic mapping, Grain traits, Quantitative trait locus (QTL), Sorghum
Since its introduction in the Yuan Dynasty, sorghum has become essential for producing Maotai-flavor liquor in China, creating high demand and necessitating specific grain traits suitable for brewing. Scientists from Guizhou Academy of Agricultural Sciences and Zhejiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences leveraged quantitative trait locus (QTL) mapping to enhance sorghum breeding. By analyzing a recombinant inbred line (RIL) population, researchers identified 20 QTLs across various environments, affecting traits such as grain size, shape, and weight. These findings align with more than 180 previously reported QTLs for sorghum grain traits, validating the effectiveness of QTL mapping for understanding complex genetic influences on brewing-specific characteristics in sorghum.
Among the identified QTLs, those on chromosomes 1, 2, 3, and 4 coincide with loci reported in previous studies, while six QTLs appear novel. These newly detected QTLs may reflect unique genetic variation in the Chinese glutinous sorghum variety HYZ, which was part of this study’s mapping population. Candidate genes within these QTL intervals share homology with known rice genes regulating grain size and weight, underscoring potential applications for sorghum. Notable candidates include Sobic.001G455900, similar to rice’s OsMADS1, which influences grain size, and Sobic.004G214100, associated with cell wall biosynthesis. These results mark significant progress in sorghum genetics, setting the stage for precise breeding strategies to optimize grain characteristics in brewing sorghum, meeting rising Maotai-flavor liquor demands.
SorghumBase examples:
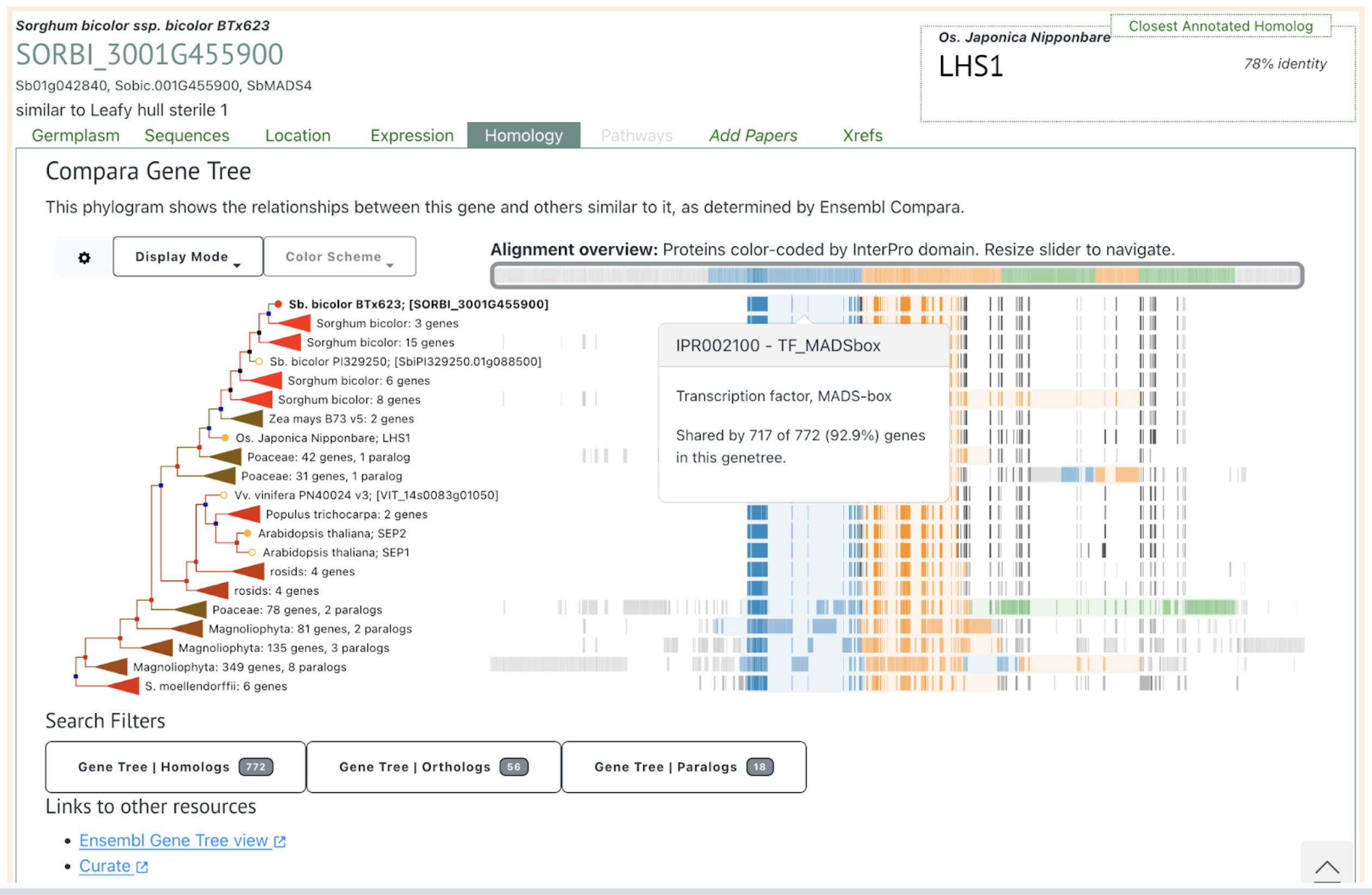

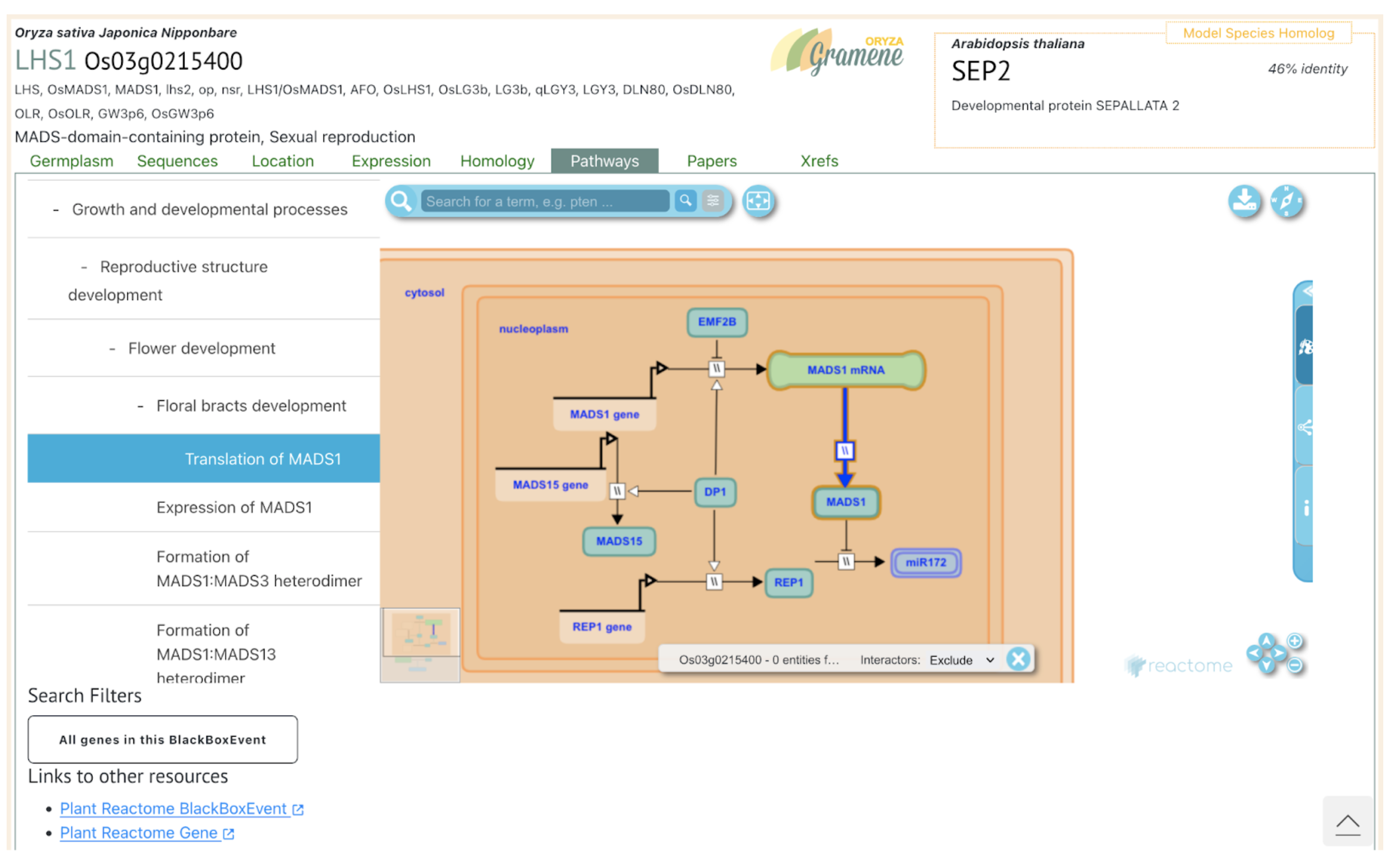
Reference:
Cao N, Ding Y, Xu J, Cheng B, Gao X, Li W, Zou G, Zhang L. QTL analysis of sorghum grain traits based on high-density genetic map. J Appl Genet. 2024 Sep 21. PMID: 39305455. doi: 10.1007/s13353-024-00904-w. Read more