This study elucidates the genetic architecture of sorghum plant height by characterizing major dwarfing genes (Dw1–Dw3), revealing their additive effects, allelic diversity, and the potential role of undiscovered minor-effect loci in shaping dwarf phenotypes.
Keywords: Chinese landraces, Sorghum bicolor, dwarfing genes, genetic analysis, plant height regulation
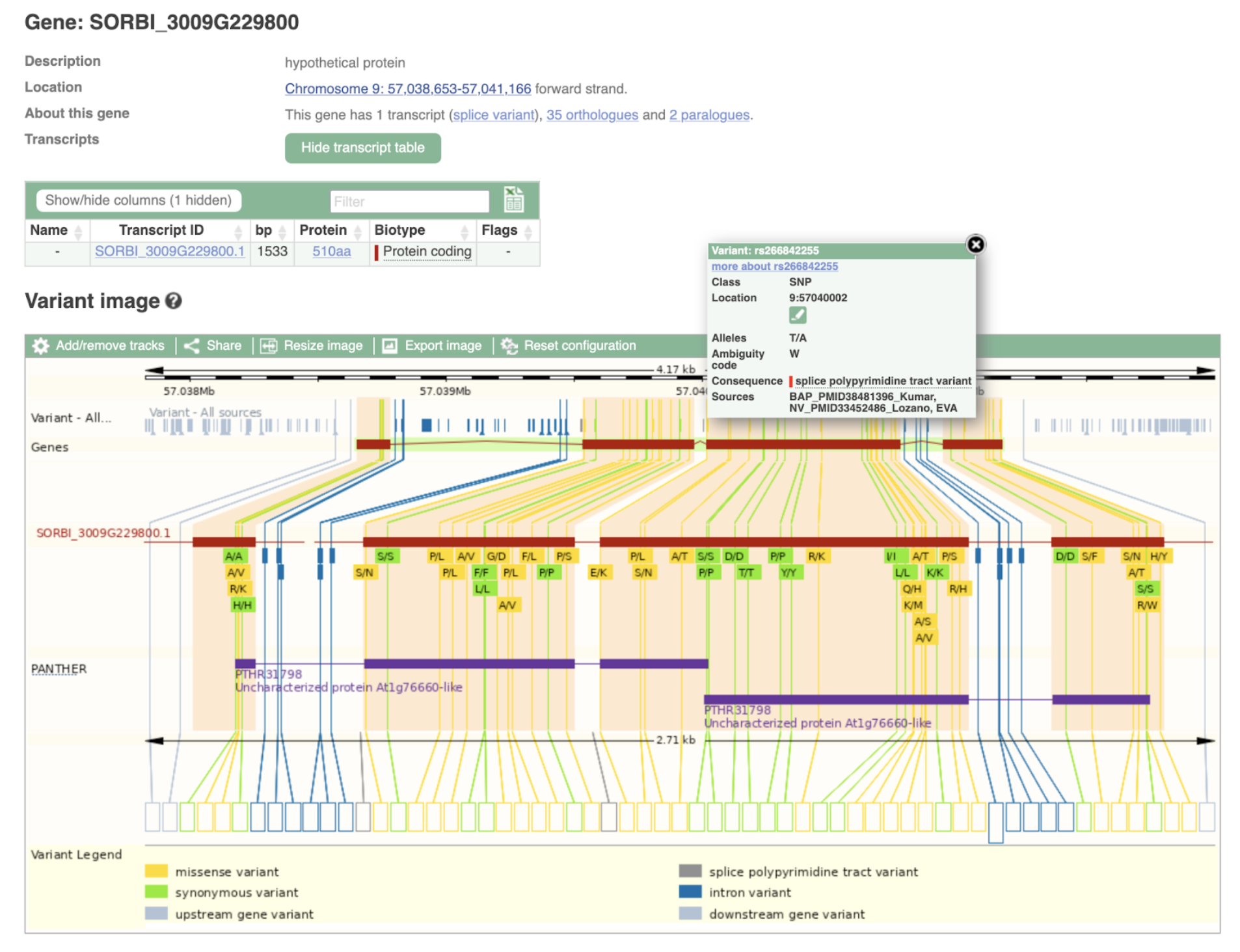
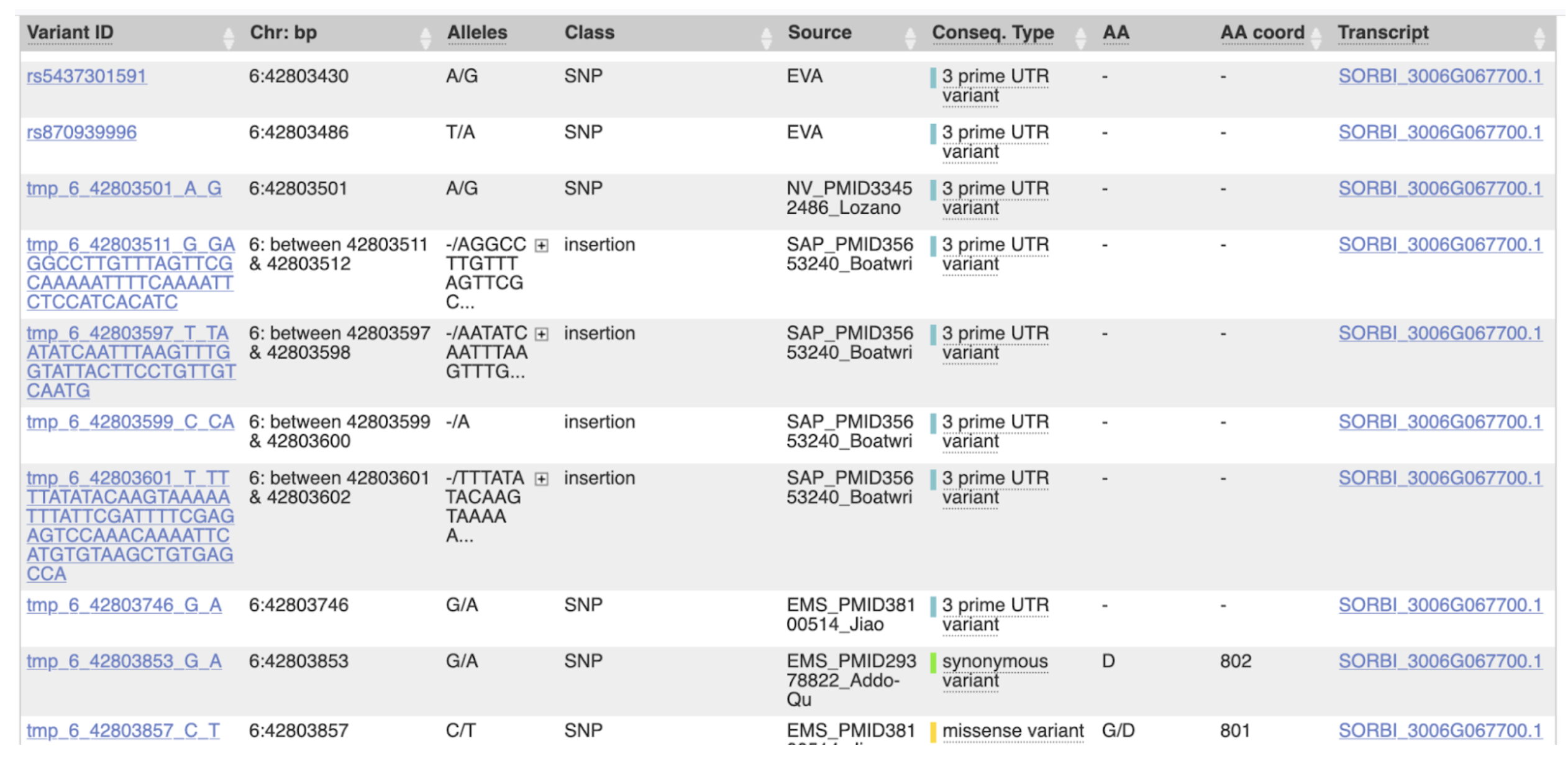
Plant height is a key agronomic trait in sorghum, influencing lodging resistance, harvest efficiency, and overall yield stability. Historically, four major dwarfing genes—Dw1 through Dw4—have been identified as regulators of internode length, which directly controls plant height. Dw1, Dw2, and Dw3 have been successfully mapped and cloned on chromosomes 9, 6, and 7, respectively, while Dw4 remains uncloned but is hypothesized to reside on chromosome 6. While single allelic mutations have been identified at the dw1 and dw2 loci, dw3 exhibits notable allelic heterogeneity, with at least seven known mutant variants. These include insertions, deletions, and point mutations, though several key alleles are absent in Chinese landraces, suggesting geographic divergence in sorghum germplasm. The lack of a standardized genotyping protocol for detecting all three major dwarfing genes has hindered high-throughput breeding efforts, underscoring the need for robust, unified molecular tools.
Recent studies conducted by scientists from Liaoning Academy of Agricultural Sciences have systematically assessed the distribution and genetic effects of Dw1–Dw3 in Chinese sorghum, revealing a low frequency of dwarfing alleles in elite germplasm and highlighting Dw3 as the most impactful locus. F2 segregation analyses of triple mutants (dw1dw2dw3) established additive and dominant effects among the genes, with dw3 contributing the most pronounced height reduction. Interestingly, some dwarf phenotypes were observed in accessions with wild-type alleles at all three loci, implying the presence of undiscovered minor-effect genes. These findings offer new insights into the polygenic regulation of plant height and establish a genetic framework for multi-gene pyramiding, advancing precision breeding strategies in sorghum.
SorghumBase examples:
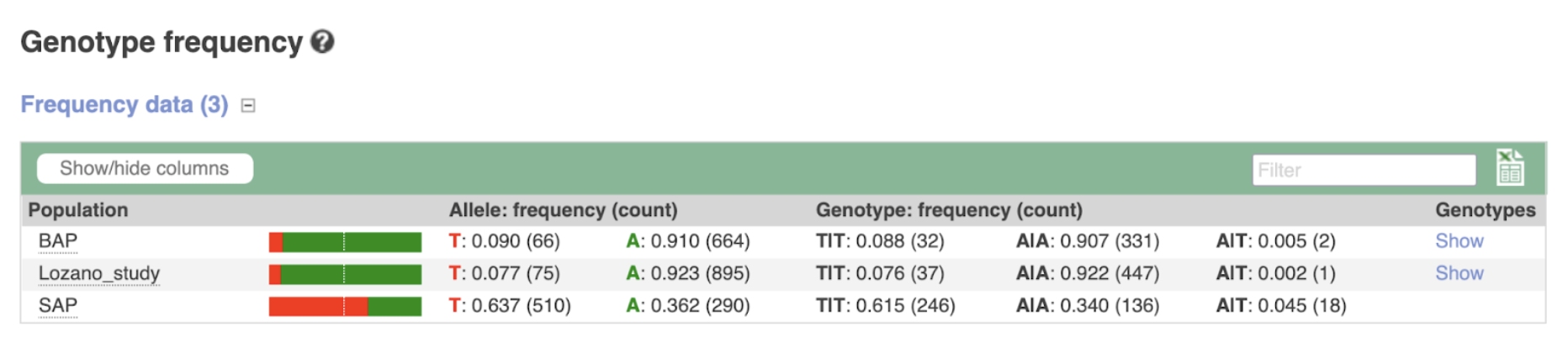
Research highlights on Sorghumbase have showcased emerging insights into the genetic architecture of dwarfing loci in sorghum, with a particular focus on the Dw1, Dw2, and Dw3 genes. These loci, which play major roles in regulating plant height, have been revisited in light of pan-genome assemblies, high-coverage re-sequencing, and new phenotypic associations. For example, the Dw3 locus was featured in a pan-genome study uncovering novel structural variants associated with stable dwarfing alleles, while a whole-genome sequencing effort of 400 SAP accessions revealed new SNP-trait associations for height. Additionally, efforts to identify deleterious edits in Dw1–Dw3 provide candidate variants for breeding and precision trait control. The variant views and genotype frequencies presented below build upon those findings, highlighting key polymorphisms across the three major dwarfing loci in different germplasm panels.
Reference:
Wang P, Liang B, Li Z, Chen L, Liu K, Wang L, Zhang L, Lu X. Genetic Dissection of Sorghum Dwarfism Through Systematic Screening of Dw1–Dw3 Alleles in Chinese Germplasm. Plants (Basel). 2025 Jun 3;14(11):1703. PMID: 40508377. doi: 10.3390/plants14111703. Read more