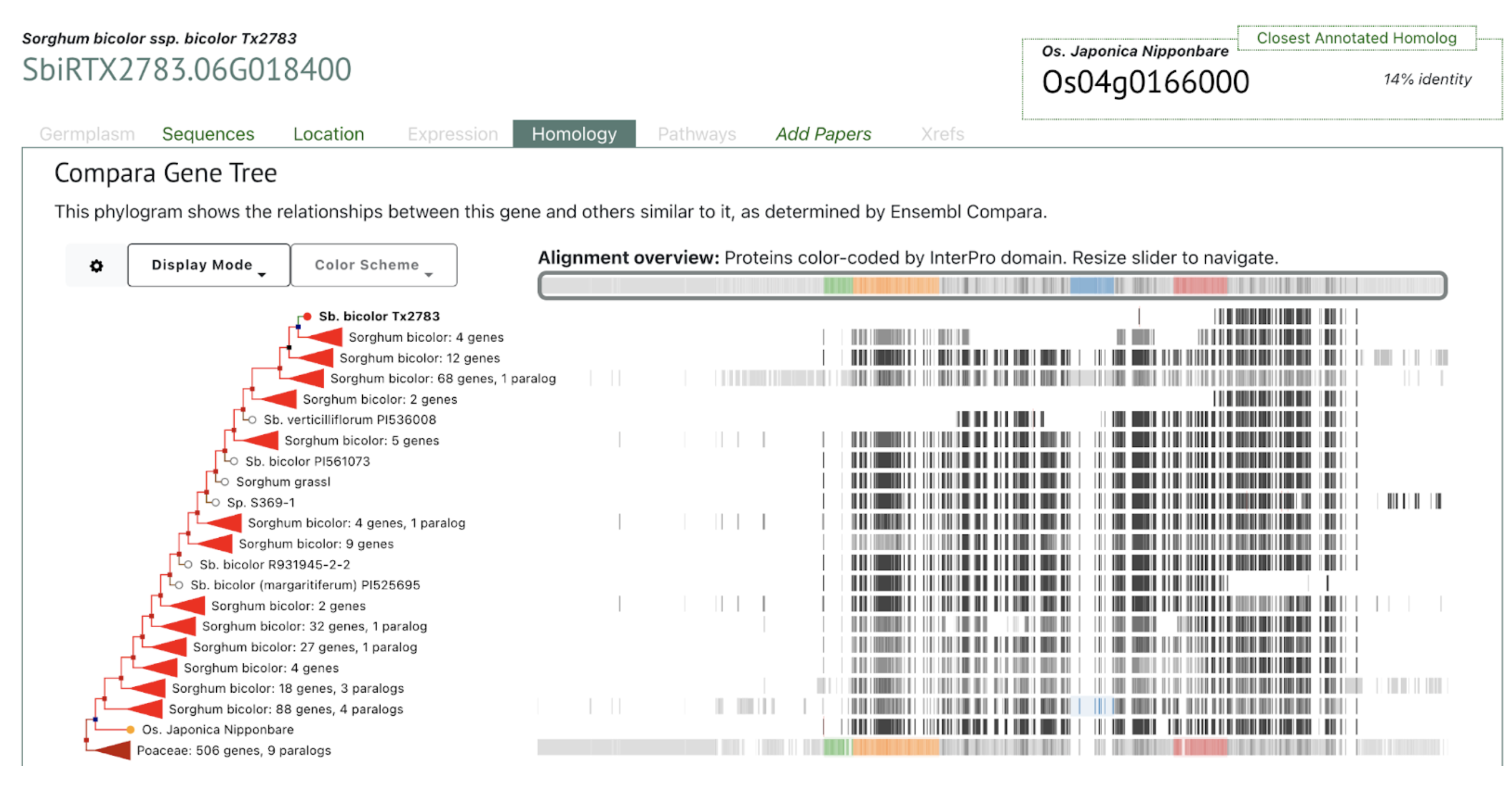
Researchers identified a novel sorghum aphid resistance QTL (qMsa-6) overlapping RMES1 and highlights SbiRTX2783.06G018400 as a key candidate gene, providing molecular targets for breeding durable, aphid-resistant sorghum.
Keywords: BSA-seq, InDel, Melanaphis sacchari, QTL, Sorghum bicolor
The sorghum aphid (Melanaphis sacchari) is a destructive pest that threatens sorghum production across Asia, Africa, Australia, and South America, contributing to yield losses of up to 40% annually and imposing global economic costs exceeding $470 billion. Although insecticides remain the dominant control method, reliance on chemical inputs risks resistance development and environmental harm, underscoring the importance of genetic resistance in sorghum improvement. Recent advances in genomics have accelerated the identification of resistance loci and candidate genes, particularly through quantitative trait locus (QTL) mapping and transcriptomic analyses. Key discoveries include four resistance QTLs on chromosome 6 and the widely studied RMES1 gene, which confers durable aphid resistance. Additional loci, such as RMES2 on chromosome 9, have been shown to act synergistically with RMES1, highlighting the polygenic and multilayered nature of sorghum’s defense mechanisms.
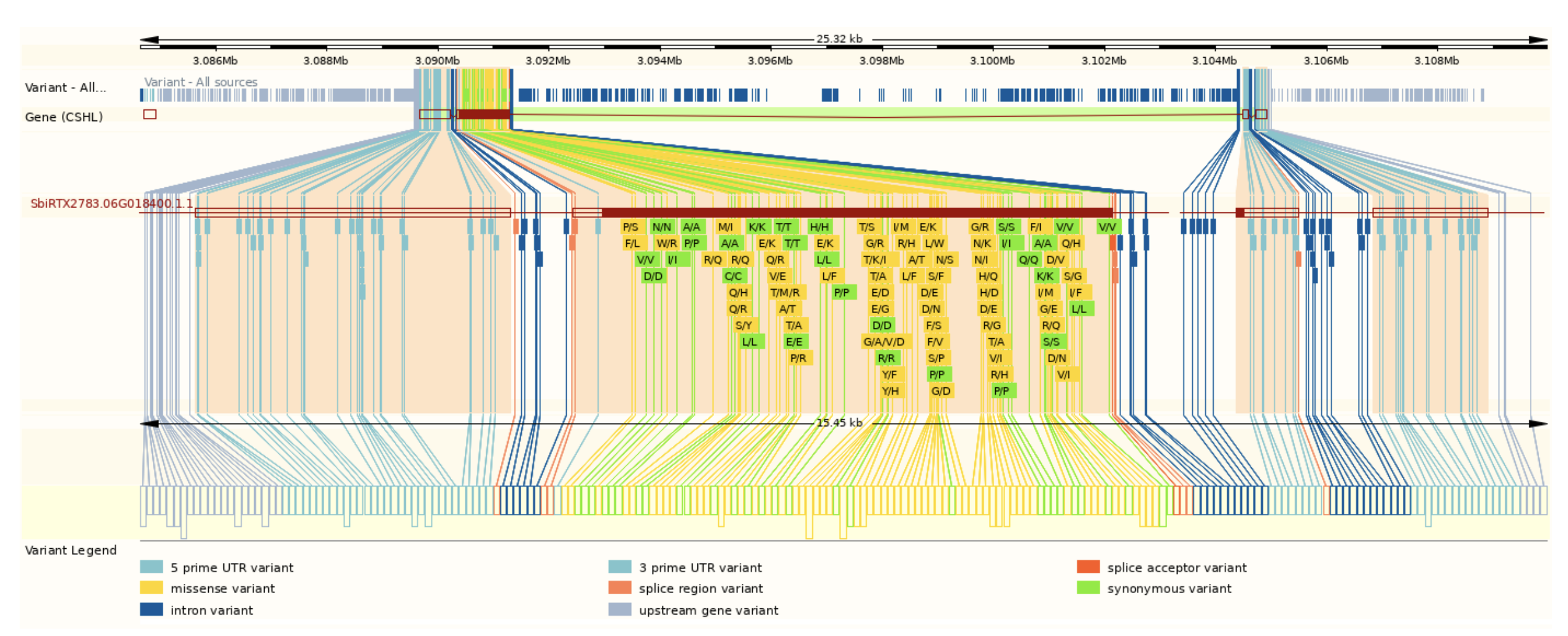
Researchers from Anhui Science and Technology University and Anhui Province International Joint Research Center of Forage Bio-breeding mapped a novel QTL (qMsa-6) to a 124 kb region on chromosome 6 overlapping RMES1, providing higher resolution and pinpointing resistance hotspots that can be targeted in molecular breeding. Candidate gene analysis identified ten genes within this region, seven of which contain NB-ARC domains characteristic of plant resistance (R) genes. These genes, commonly associated with nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat (NBS-LRR) proteins, play a central role in effector-triggered immunity (ETI) and pathogen recognition. Notably, SbiRTX2783.06G018400 exhibited strong induction upon aphid feeding, suggesting a critical role in defense signaling, likely acting in concert with other R genes to form a multilayered immune response. These findings provide both theoretical and applied insights for sorghum breeding, offering opportunities for marker-assisted selection (MAS) and gene editing to develop durable, aphid-resistant varieties. By integrating resistance loci such as qMsa-6 with cutting-edge biotechnologies, sustainable sorghum production can be advanced while reducing pesticide dependence and associated ecological impacts.
SB Examples:
Reference:
Du J, Zou K, Shen Q, Liu Y, Guan M, Wang T, Wu D, Wang L, Wang Y, Li J. Identification of QTLs for aphid (Melanaphis sacchari) resistance in sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) based on BSA-seq and analysis of candidate genes. BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Aug 16;25(1):1081. PMID: 40819068. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-07028-1. Read more